Address Arithmetic
If p is a pointer to some element of an array, then p++ increments p to point to the next element, and p+=i increments it to point i elements beyond where it currently does. These and similar constructions are the simplest forms of pointer or address arithmetic.
C is consistent and regular in its approach to address arithmetic; its integration of pointers, arrays, and address arithmetic is one of the strengths of the language. Let us illustrate by writing a rudimentary storage allocator. There are two routines. The first, alloc(n), returns a pointer to n consecutive character positions, which can be used by the caller of alloc for storing characters. The second, afree(p), releases the storage thus acquired so it can be reused later. The routines are "rudimentary" because the calls to afree must be made in the opposite order to the calls made on alloc. That is, the storage managed by alloc and afree is a stack, or last-in, first-out. The standard library provides analogous functions called malloc and free that have no such restrictions; in Section 8.7 we will show how they can be implemented.
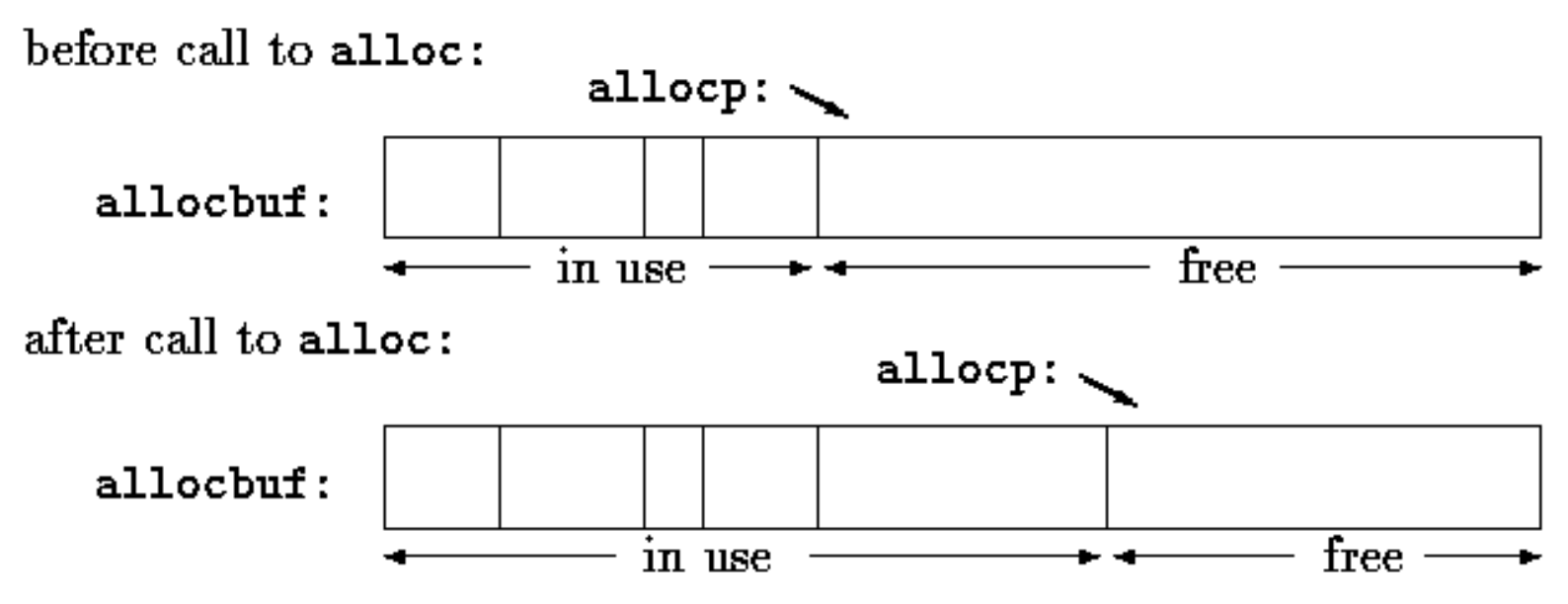
The easiest implementation is to have alloc hand out pieces of a large character array that we will call allocbuf. This array is private to alloc and afree. Since they deal in pointers, not array indices, no other routine need know the name of the array, which can be declared static in the source file containing alloc and afree, and thus be invisible outside it. In practical implementations, the array may well not even have a name; it might instead be obtained by calling malloc or by asking the operating system for a pointer to some unnamed block of storage.
The other information needed is how much of allocbuf has been used. We use a pointer, called allocp, that points to the next free element. When alloc is asked for n characters, it checks to see if there is enough room left in allocbuf. If so, alloc returns the current value of allocp (i.e., the beginning of the free block), then increments it by n to point to the next free area. If there is no room, alloc returns zero. afree(p) merely sets allocp to p if p is inside allocbuf.
#define ALLOCSIZE 10000 /* size of available space */
static char allocbuf[ALLOCSIZE]; /* storage for alloc */
static char *allocp = allocbuf; /* next free position */
char *alloc(int n) /* return pointer to n characters */
{
if (allocbuf + ALLOCSIZE - allocp >= n) { /* it fits */
allocp += n;
return allocp - n; /* old p */
} else { /* not enough room */
return 0;
}
}
void afree(char *p) /* free storage pointed to by p */
{
if (p >= allocbuf && p < allocbuf + ALLOCSIZE) {
allocp = p;
}
}
In general a pointer can be initialized just as any other variable can, though normally the only meaningful values are zero or an expression involving the address of previously defined data of appropriate type. The declaration:
static char *allocp = allocbuf;
defines allocp to be a character pointer and initializes it to point to the beginning of allocbuf, which is the next free position when the program starts. This could also have been written
static char *allocp = &allocbuf[0];
since the array name is the address of the zeroth element.
The test:
if (allocbuf + ALLOCSIZE - allocp >= n) {} /* it fits */
checks if there's enough room to satisfy a request for n characters. If there is, the new value of allocp would be at most one beyond the end of allocbuf. If the request can be satisfied, alloc returns a pointer to the beginning of a block of characters (notice the declaration of the function itself). If not, alloc must return some signal that there is no space left. C guarantees that zero is never a valid address for data, so a return value of zero can be used to signal an abnormal event, in this case no space.
Pointers and integers are not interchangeable. Zero is the sole exception: the constant zero may be assigned to a pointer, and a pointer may be compared with the constant zero. The symbolic constant NULL is often used in place of zero, as a mnemonic to indicate more clearly that this is a special value for a pointer. NULL is defined in <stdio.h>. We will use NULL henceforth.
Tests like:
if (allocbuf + ALLOCSIZE - allocp >= n) {} /* it fits */
and:
if (p >= allocbuf && p < allocbuf + ALLOCSIZE)
show several important facets of pointer arithmetic. First, pointers may be compared under certain circumstances. If p and q point to members of the same array, then relations like ==, !=, <, >=, etc., work properly. For example,
p < q
is true if p points to an earlier element of the array than q does. Any pointer can be meaningfully compared for equality or inequality with zero. But the behavior is undefined for arithmetic or comparisons with pointers that do not point to members of the same array. (There is one exception: the address of the first element past the end of an array can be used in pointer arithmetic.)
Second, we have already observed that a pointer and an integer may be added or subtracted. The construction:
p + n
means the address of the n-th object beyond the one p currently points to. This is true regardless of the kind of object p points to; n is scaled according to the size of the objects p points to, which is determined by the declaration of p. If an int is four bytes, for example, the int will be scaled by four.
Pointer subtraction is also valid: if p and q point to elements of the same array, and p<q, then q-p+1 is the number of elements from p to q inclusive. This fact can be used to write yet another version of strlen:
/* strlen: return length of string s */
int strlen(char *s)
{
char *p = s;
while (*p != '\0')
p++;
return p - s;
}
In its declaration, p is initialized to s, that is, to point to the first character of the string. In the while loop, each character in turn is examined until the '\0' at the end is seen. Because p points to characters, p++ advances p to the next character each time, and p-s gives the number of characters advanced over, that is, the string length. (The number of characters in the string could be too large to store in an int). The header <stddef.h> defines a type ptrdiff_t that is large enough to hold the signed difference of two pointer values. If we were being cautious, however, we would use size_t for the return value of strlen, to match the standard library version. size_t is the unsigned integer type returned by the sizeof operator.
Pointer arithmetic is consistent: if we had been dealing with floats, which occupy more storage that chars, and if p were a pointer to float, p++ would advance to the next float. Thus we could write another version of alloc that maintains floats instead of chars, merely by changing char to float throughout alloc and afree. All the pointer manipulations automatically take into account the size of the objects pointed to.
The valid pointer operations are assignment of pointers of the same type, adding or subtracting a pointer and an integer, subtracting or comparing two pointers to members of the same array, and assigning or comparing to zero. All other pointer arithmetic is illegal. It is not legal to add two pointers, or to multiply or divide or shift or mask them, or to add float or double to them, or even, except for void *, to assign a pointer of one type to a pointer of another type without a cast.